You’ve come to the perfect place if you’ve ever wanted to experiment with sewing by making your outfits or modifying existing ones. Learn all you need to know to get started sewing with the help of this thorough tutorial. This article will serve as your go-to reference, equipping you with the knowledge to realize your creative potential from the ground up.
First, we’ll cover the basics of sewing, such as choosing a machine, gathering the supplies you’ll need, and preparing a work area. Next, we’ll study the fundamental sewing skills that are the backbone of every creation. You will feel comfortable performing professional-looking stitches, from threading the machine and sewing straight lines to making beautiful seams and completing edges.
11 things to think about before buying any sewing machine:
When shopping for a sewing machine, it’s critical to research to save money on the right one. Here are ten things to think about before making a purchase:
1. Purpose:
Determine the primary reason for purchasing a sewing machine. Are you a beginner looking for basic stitching or an expert looking for sophisticated features? Clarify your needs to select a suitable device.
2. Budget:
Create a budget that meets your needs. Sewing machines vary in price, so knowing your financial constraints will help narrow your selections.
3. Sewing Experience:
Think about your sewing abilities. A high-end, sophisticated machine may be overkill if you’re starting out. Choose a model appropriate for your skill level and allows for future progress.
4. Features:
- List the characteristics you need in a sewing machine.
- Consider stitch types, an automatic threader, buttonhole styles, needle placements, and speed control.
- Make a list of the features that are most important to you.
5. Versatility:
Determine the range of textiles and projects you wish to work with. Some machines are designed to work with specific materials, such as heavy-duty leather equipment or quilting machines. Check that the device is capable of handling your chosen projects.
6. Brand and Reputation:
Research different sewing machine companies and their reputations for quality, dependability, and customer service. Read reviews and ask advice from experienced sewers.
7. User-Friendliness:
Choose a simple machine to install, run, and maintain. Complex devices with a steep learning curve may put off novices or those with limited time.
8. Size and portability:
Consider the space available in your sewing location. A compact and lightweight model may be ideal if you have limited room or intend to relocate the machine regularly.
9. Warranty and Service:
Confirm the manufacturer’s warranty period. In addition, to ensure long-term support, investigate the availability of approved service centers and the cost of repairs.
10. Test and Compare:
Visit a local store and try various sewing machine models. Compare their performance, noise level, and general comfort to determine which machine is best for you.
11. Accessories and Attachments:
Consider the accessories and attachments that come with the sewing machine or may be purchased separately. Presser feet, extension tables, walking feet, embroidery attachments, and other items may be included. Consider these accessories’ added cost and availability, as they can improve your sewing skills and broaden the choice of projects you can work on.
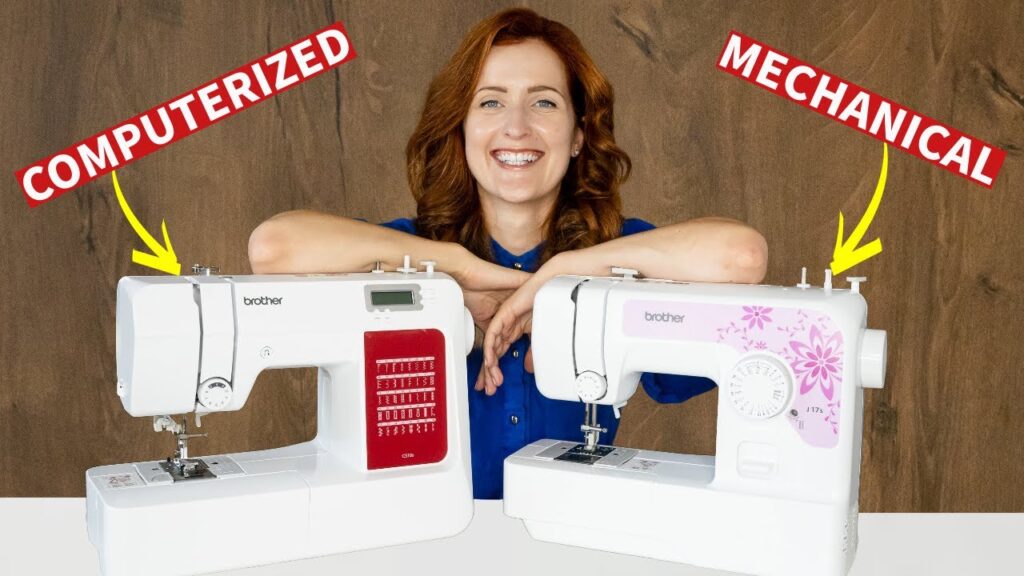
Mechanical vs Computerized Sewing Machine: Which Is Better?
Mechanical sewing machines are operated manually by dials, knobs, and levers. They are typically simpler in terms of functionality and have fewer built-in capabilities. They are appropriate for sewing beginners or those who want a more conventional approach. Computerized sewing machines are outfitted with cutting-edge technology and electronic components.
They have a variety of capabilities, including programmed stitch patterns, touch screens, automatic thread cutters, and built-in monogramming fonts. Experienced sewers or those who demand precise and intricate stitching frequently prefer computerized devices.
Standard Features of Any Sewing Machine at Home:
Stitch Options: Look for machines that offer several stitch options, such as straight, zigzag, buttonholes, and decorative stitching.
Adjustable Stitch Length and Breadth: Modifying your stitches for different fabric kinds and techniques are made possible by adjusting stitch length and breadth.
Automatic Needle Threader: This feature makes threading the needle easier while saving time and decreasing eye strain.
Drop-in Bobbin System: A drop-in bobbin system makes inserting and removing the bobbin easier and offers convenient access for threading and monitoring thread supply.
Adjustable Presser Foot Pressure: This function allows you to change the presser foot’s pressure on the cloth, ensuring even stitching on a variety of fabric thicknesses.
Free Arm Capability: The free arm is a removable or retractable part of the sewing machine that allows for easy stitching of cylindrical goods such as sleeves and cuffs.
Reverse Stitching: To reinforce seams or generate backstitches at the beginning and end of a seam, the machine should feature a reverse stitch option.
A built-in light illuminates the sewing area, making seeing the cloth and stitches easier.
Hand Operated Sewing Machines
Hand-operated sewing machines are small and easy to carry. They can be used to sew by hand without electricity. These machines are usually small and easy to use, which makes them suitable for repairs on the go, small jobs, or when there is no power. They move the needle and make stitches with the help of a hand crank or a handle. Hand-operated sewing machines may be slower or have as many features as electric sewing machines. Still, they are helpful for basic sewing chores, quick fixes, or people who like a more traditional and hands-on sewing experience. They are beneficial in an emergency or when you need a compact way to sew.
Home Sewing Machine:
A home sewing machine is a multifunctional and easy-to-use instrument for domestic use. It enables people to design and modify their clothes, work on sewing projects, and engage in creative activities. Home sewing machines come with a variety of stitches, adjustable settings, and features that make sewing fun and accessible to both novice and experienced sewers. They can handle various fabric kinds and allow you to experiment with new sewing techniques, adjustments, and creative projects. A home sewing machine is crucial for bringing your creative ideas to life, whether you’re a hobbyist or a dedicated sewer.
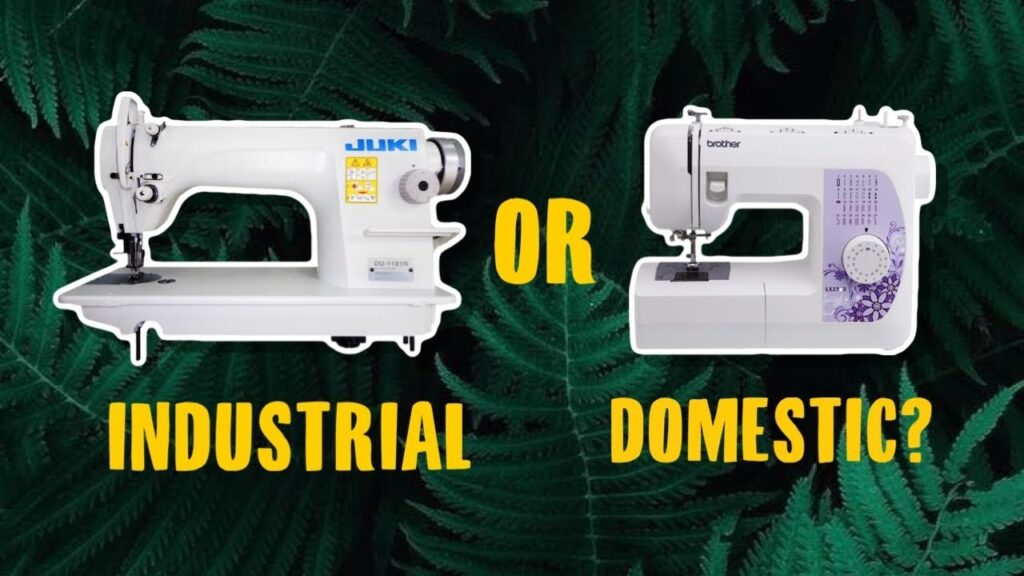
Domestic vs Industrial Sewing Machines:
Domestic and industrial sewing machines serve various functions in the sewing business. Household appliances are intended for personal and small-scale undertakings and are versatile and straightforward. They can handle multiple fabric kinds and offer stitch options suited for typical sewing operations. In contrast, industrial machines are designed for high-volume production in commercial environments. They are more robust and powerful, capable of stitching through thick fabrics and numerous layers quickly and precisely. Industrial machines excel in efficiency, durability, and specific tasks, making them indispensable for enterprises that engage in mass production and demanding sewing operations. While domestic machines are appropriate for individual sewers, hobbyists, and small enterprises, industrial machines are required for larger-scale manufacturing and professional stitching.
Things a home sewing machine can achieve that an industrial model cannot:
Portability: Because home sewing machines are compact and lightweight, they are portable and easy to move about. This can be useful if you transport your sewing machine to multiple locations or keep it in a small space.
Versatility in Fabric Types: Home sewing machines are often intended to handle a wide range of textiles, including lightweight and medium-weight fabrics such as cotton, linen, silk, and some knits. They are appropriate for ordinary sewing, modifications, and handicraft projects that use a variety of fabric kinds.
Small-Scale Projects: Home sewing machines are ideal for smaller-scale operations such as clothing repairs, garment modifications, and basic dressmaking. They are great for creating personal goods or gifts for friends and relatives.
Cost: Home sewing machines are often less expensive than industrial machines, giving them a more accessible alternative for people who sew as a hobby or for personal use.
Industrial or Commercial Sewing Machine
Industrial sewing machines are heavy-duty machines built for high-volume output in professional environments. These machines are designed to handle heavy materials, many layers, and continuous operation, making them perfect for companies that produce garments, upholstery, automobile interiors, or other textile items. Compared to domestic sewing machines, industrial sewing machines have incredible speed, power, and specialized functionality. They can quickly stitch through thick materials, give exact and consistent stitches, and provide various possibilities for multiple applications. Industrial or commercial sewing machines, with their durability, dependability, and ability to handle demanding stitching jobs, are crucial instruments for delivering efficient and professional-grade outcomes in large-scale production operations.
Things an industrial machine can achieve that a household model cannot:
Heavy-Duty Textiles: Industrial sewing machines are built to work with heavy-duty materials like leather, denim, canvas, and upholstery textiles. They have more powerful motors and machinery that can easily sew through numerous layers of thick fabric.
Continuous Operation: Industrial machinery is built to be used continuously for long periods of time. They feature a sturdy build and components that can withstand high-volume production demands without overheating or having mechanical problems.
Larger Bobbins and Thread Capacity: Industrial machines typically have larger bobbins and higher thread capacity, reducing the frequency of bobbin changes. This is useful for sewing jobs that require long, continuous stitching.
Durability and longevity: Industrial machines are designed to resist hard use and last for many years. They are made with solid materials and components, making them more durable and capable of withstanding the demands of business environments.
2 Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Home or Industrial Sewing Machine
Here are two things to keep in mind as you weigh the pros and downsides of home vs. industrial sewing machines:
Dimensions of Room and Sewing Area:
Check out how much room you have in your workshop or sewing room. Compared to household sewing machines, industrial ones are bigger and bulkier. They might have supplementary parts like a more substantial table or motor stand. Ensure you have adequate space for the machine you choose, providing easy access and a well-organized work area.
Types of Motors:
Alternating Current (AC) Motor (Clutch Motor):
Industrial sewing machines frequently utilize clutch motors. Sewing speeds are increased by their incredible power and torque. However, the clutch mechanism in these vehicles wears out quickly, making them noisier and more high-maintenance.
Direct Current (DC) Motor (Servo Motor):
Servo motors are rapidly replacing conventional motors in commercial sewing machines. Compared to clutch motors, they provide more accurate speed regulation, reduced noise levels, and greater efficiency. For more precise control over the sewing pace, servo motors are the best option for delicate or complex sewing projects.
What are sewing machines constructed of precisely?
Sewing machines have several parts and materials. Metal, plastic, and other components make it durable and comfy. Metal frames stabilize and support the machine. Sewing pressure and vibrations require robust materials like cast iron or metal.
Plastic or metal body casings protect internal parts. Plastic covers make machines lighter and easier to carry. Metal casings are tougher. The needle bar and presser foot guide the cloth and needle in a sewing machine. Steel, or stainless steel, is used to make these pieces durable and sturdy.
Sewing machine motors are metal or plastic. The motor case lets the motor breathe and prevents overheating. Clutch motors (AC motors) and servo motors (DC motors) have different materials and functions. Metal bobbin cases and shuttles, which hold the bobbin and thread, endure longer and make thread movement easier. To maintain durability, the machine’s gears and pulleys that drive and regulate functions are usually steel or brass.
Digital sewing machines have plastic buttons and control panels. These elements enable you to modify the stitch and settings and display crucial information on an LCD screen. Metal and plastic make sewing machines strong, stable, and lightweight. Sewers can use the machine safely and effectively with these materials.
FAQs:
What is a sewing guide?
A sewing guide is a resource or tool that provides instructions, tips, and techniques to help individuals with their sewing projects. It serves as a reference or reference book for sewers of all levels of expertise.
What can I find in a sewing guide?
Sewing guides typically cover a wide range of topics related to sewing. They may include information on basic sewing techniques, fabric selection, pattern reading, machine operation, garment construction, fitting, sewing terminology, and troubleshooting common sewing issues.
Are sewing guides only for beginners?
No, sewing guides are helpful for sewers of all skill levels. While beginners can benefit from the essential information and guidance in sewing guides, more experienced sewers can also find advanced techniques, tips, and inspiration to enhance their sewing skills and tackle more complex projects.
Are sewing guides available in different formats?
Yes, sewing guides are available in various formats to cater to different preferences. They can be found in printed books, e-books, online tutorials, video tutorials, and sewing blogs. Some sewing machine manufacturers also provide user manuals that serve as sewing guides specific to their machine models.
Where can I find sewing guides?
Sewing guides can be found in bookstores, craft stores, and online retailers. Many sewing websites, blogs, and forums offer free tutorials and guides. Libraries may also have sewing books and resources available for borrowing. Additionally, sewing magazines often feature articles and principles related to specific sewing topics.
Can a sewing guide replace sewing lessons or classes?
While sewing guides provide valuable information and guidance, they may still need to replace the hands-on experience and personalized instruction provided by sewing lessons or classes. Taking sewing lessons or attending classes can offer the opportunity to learn from experienced instructors.
Conclusion:
In summary, the world of sewing is your oyster once you have this complete handbook on your side. You’ll find helpful information in this sewing guide whether you’re just starting or have years of expertise under your needle. Get your needle threaded and your sewing machine ready because the fun is about to begin! Let the sewing begin!