It is hard to emphasize how crucial a well-functioning needle is when stitching. Unfortunately, sewing machine needle problems occasionally arise for even the most seasoned sewers. To ensure seamless and frustration-free sewing sessions, it is essential to comprehend and address these issues. To maintain your stitching projects on schedule, we will examine the most frequent sewing machine needle issues, their causes, and workable solutions in this post.
How Important a Good Needle Is?
The sewing machine needle is a crucial element directly impacting the stitching quality. Understanding the importance of choosing the right needle for your particular project. Numerous issues, like fabric damage and skipped stitches, can be caused by a broken or inappropriate needle.
Sewing Machine Needle Problems:
Your sewing tasks may need help with needle issues with your sewing machine. Broken threads skipped stitches, and even fabric damage can be caused by a broken needle. For efficient and effective sewing, it’s crucial to comprehend and address these needle-related problems. This thorough article review 25 typical sewing machine needle issues, their causes, and practical fixes to help you overcome these difficulties and produce high-quality stitching.
Needle Breakage Issues
Incorrect Needle Type:
Determine the ramifications of using the incorrect needle type for your fabric and stitching technique, such as breaking owing to insufficient strength or a needle form that is not appropriate.
Improper Needle Size:
Discover how too thin or too thick needles for the fabric can bend or shatter.
Improper Needle Insertion:
Learn the significance of proper needle insertion and how poor placement can result in needle breakage during stitching.
Sewing Through Thick Layers:
Understand the difficulties of stitching through numerous layers of fabric and how it might result in needle breakage. Learn how to deal with this problem.
Stitching Issues
Skipped Stitches:
Determine the causes of skipped stitches, such as a dull or bent needle, an improper needle-thread combination, or a timing problem with the sewing machine. To address this issue, learn troubleshooting procedures.
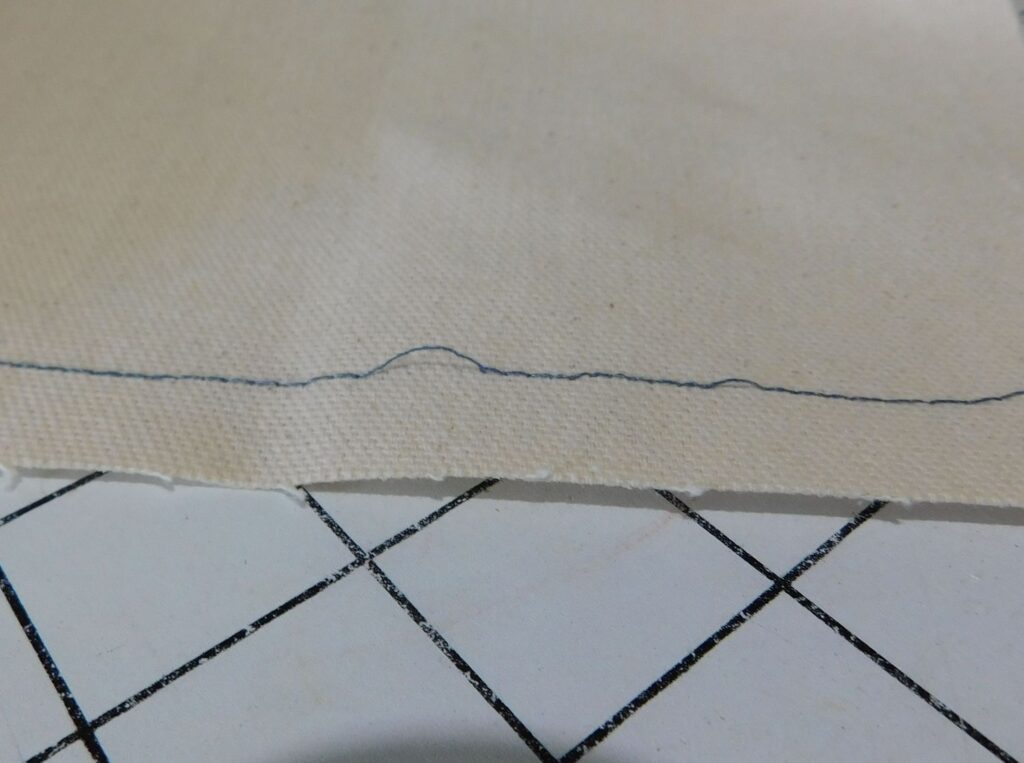
Uneven Stitches:
Investigate the causes of uneven stitches, such as inconsistent fabric feeding, incorrect tension settings, or using the wrong needle for the fabric.
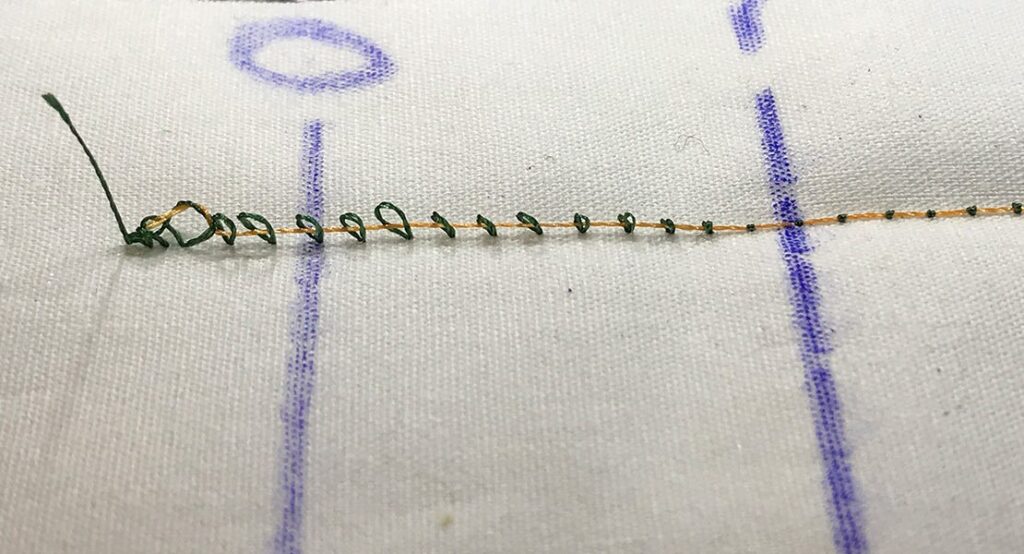
Looped or Bunched Stitches:
Recognize the causes of loops or bunched stitches, such as poor threading, inappropriate tension settings, or incorrect needle or thread use.
Puckered Fabric:
Learn why fabric puckering happens and how it can be caused by needle difficulties such as using a too-thick needle or the incorrect needlepoint for the cloth.
Thread Problems
Thread Breakage:
Determine the causes of thread breakage, such as a worn-out needle, the use of low-quality thread, wrong tension settings, or inappropriate threading procedures. Learn how to troubleshoot thread breakage and how to avoid it.
Thread Shredding:
Investigate the causes of thread shredding, such as using a needle with a small eye, using the incorrect needle size, or using a rough needle that causes friction.
Tangles in the Thread:
Understand the causes of thread tangles during sewing, such as poor threading, inappropriate tension settings, or using a dull or damaged needle. Learn how to prevent thread tangling.
Needle Performance Issues
Dull Needle:
Learn about the drawbacks of using a dull needle, including poor stitch quality, fabric damage, and increased needle breakage. Learn how to spot the signs of a blunt needle and when to replace it.
Bent Needle:
Learn why needles can bend when sewing and how this impacts stitch formation. Learn how to avoid needle bending and achieve peak needle performance.
Needle with a Burr-edge:
Investigate the reasons for needle burrs, such as hitting pins or stitching over thick seams. Learn about the effects of a burr-edged needle on fabric and how to avoid it.
Needle Alignment and Timing Issues
Needle Strikes the Plate:
Determine what is causing the needle to strike the plate, such as a misaligned needle or an erroneous needle bar height adjustment. Learn how to deal with this problem.
Needle Strikes the Hook:
Learn why the needle may strike the hook, resulting in broken needles or timing problems. Learn how to troubleshoot and when to seek professional help.
Other Needle Issues
Needle Heat:
Learn why sewing needles can grow heated and how this affects stitch quality. Learn how to avoid excessive needle heat.
Needle Noise:
Learn about the reasons for needle noise, such as improper needle-bar clearance or problems with the sewing machine’s internal components. Learn how to reduce needle noise.
Preventive Actions
Choosing the Correct Needle:
Insist on using the proper needle type, size, and point for your cloth and sewing technique. Recognize the distinctions between universal, ballpoint, sharp, and specialty needles.
Needle Cleaning:
Learn how to properly care for your needles, including cleaning and storing them appropriately.
Needle & Thread Compatibility:
To avoid problems, understand the link between needles and threads. Learn how different thread weights and fibers affect needle performance and make adjustments accordingly.
Seeking Professional Assistance
When to Seek Professional Help:
Determine when it is appropriate to seek the help of a professional sewing machine technician to address complex needle-related concerns.
How to Get Rid of Needle Issues: Troubleshooting and Prevention Techniques
Dealing with needle difficulties when sewing can frustrate and slow your progress. However, you can effectively handle and prevent needle problems with the correct knowledge and procedures. In this post, we will walk you through the practical methods to resolving needle issues, including troubleshooting procedures and preventive measures, to ensure a smooth and trouble-free sewing experience.
Troubleshooting Needle Issues
Identify the Problem:
Examine the symptoms and problems you’re having with your needle, like breakage, skipped stitches, or thread troubles. Discover the specific needle issue to discover the best solution.
Examine the Needle Type and Size:
Ensure you use the correct needle type and size for your fabric and stitching technique. See the manufacturer’s guidelines or a needle reference guide for optimal needle selection.
Check the Needle Condition:
Look for evidence of damage, such as bending, burrs, or dullness, on the needle. If required, replace the needle.
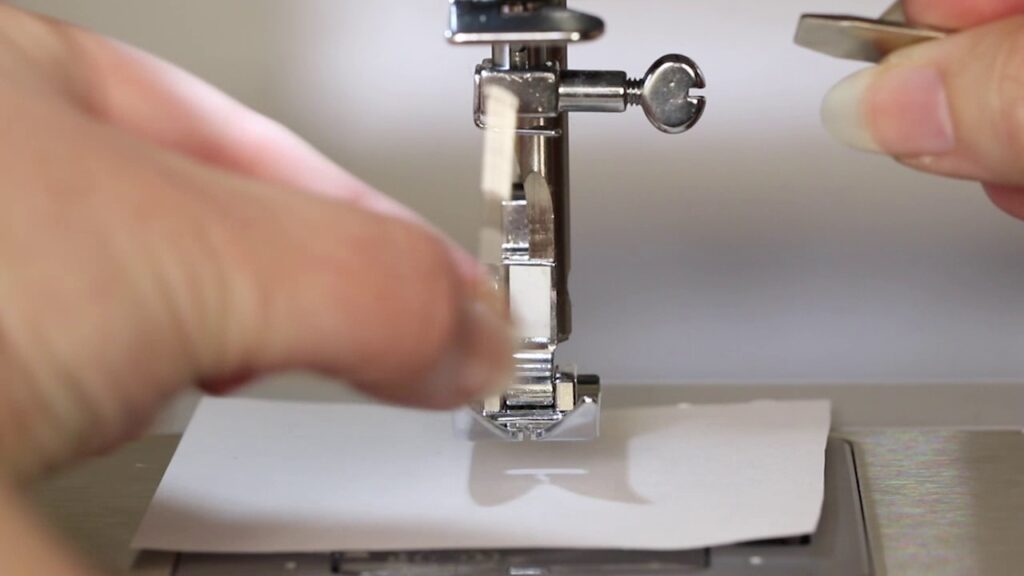
Verify for Proper Needle Insertion:
Check that the needle is correctly placed into the machine according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure it’s seated and aligned with the needle clamp or set screw.
Adjust Thread Tension:
Improper thread tension might lead to needle problems. To produce balanced stitches, experiment with altering the upper thread tension.
Cleaning and lubrication:
Clean the needle section of the machine to remove any lint, debris, or accumulation that may interfere with the needle’s effectiveness. Lubricate the machine according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Preventing Needle Issues
Select High-Quality Needles:
Use high-quality needles from respected companies to ensure the best performance and longevity. Cheap or subpar needles can result in frequent needle difficulties.
Replace Needles regularly:
Replace the needle every 8-10 hours of sewing or when beginning a new project. Needles become dull and prone to problems over time.
Use the Appropriate Needle for the Job:
Choose the best needle type, size, and point for your cloth and sewing technique. To avoid needle difficulties, different textiles necessitate various needle properties.
Proper Needle Handling Practice:
Handle needles cautiously, as dropping or mishandling them might result in bending or damage.
Thread correctly:
Follow the machine’s threading directions attentively, ensuring the thread is properly guided through the essential thread guides and tension discs. Incorrect threading can lead to needle-related issues.
Sew at a Medium Speed:
Sewing too quickly can strain the needle, potentially resulting in breakage or other problems.
Take Breaks When Sewing Thick Layers:
Take breaks when sewing through numerous layers of fabric to allow the machine’s engine and needle to cool down. This avoids needle overheating and possible damage.
Perform Routine Maintenance:
Clean your sewing machine regularly, including the needle area and bobbin case, and feed dogs to prevent debris buildup that can impair needle performance. Follow the maintenance instructions provided by the manufacturer.
How To Thread A Needle In A Sewing Machine?
Proper machine sewing requires threading a needle. Raise the presser foot and place the thread spool on the spool pin to thread the needle. Follow the machine’s threading path with the thread end. If necessary, incorporate the tension discs and take up the lever. Finally, thread the needle from front to back to correctly seat the thread in the eye. Built-in needle threaders on some sewing machines make this easier. Follow the manufacturer’s directions to use a needle threader. Threading the needle properly ensures smooth stitching and prevents needle breakage.
Why Does My Sewing Machine Needle Keep Breaking?
Frequent needle breakage might disrupt stitching tasks. This issue has many causes. The improper needle for your fabric or stitching method is one explanation. A fabric-unsuitable needle can bend or shatter. Improper needle insertion is another possibility. The needle can break the plate or hook if it isn’t fully inserted or aligned with the machine. Broken needles or sewing through heavy layers without support can also cause breakage. Incorrect thread tension, hitting pins or other complex objects while sewing, or machine timing difficulties can also damage needles. Selecting the correct needle, inserting it correctly, and checking the machine’s timing can prevent needle breakage.
What Do Sewing Machine Needle Sizes Mean?
80/12 or 110/18 are sewing machine needle sizes. American and European systems determine the needle’s size range. In the American method, the first number reflects the needle’s size range for lightweight fabrics and the second for thicker textiles. An 80/12 needle works for light to medium-weight materials, whereas a 110/18 needle works for heavyweight clothes. The European system uses metric values to indicate needle blade diameter in hundredths of a millimeter. 90 needles have 0.90 mm blade diameters. For correct stitch creation and needle selection, you must understand needle sizes.
How To Move Needle Position On Singer Sewing Machine?
Singer sewing machines use the stitch width adjustment or needle position selector to move the needle depending on the model. Find your Singer sewing machine’s needle position control. Some types have a needle position selector, while others have a stitch width dial or lever. Find the power in the machine’s handbook. Once identified, move the needle left or right to your chosen position. Topstitching, edge stitching, and seam allowances benefit from this functionality. To sew well, try different needle locations.
How To Use A Needle Threader On A Sewing Machine?
Those with weak eyesight or dexterity may benefit from a needle threader. Follow these instructions to thread a sewing machine needle. Raise the needle to its highest point using the handwheel or machine controls. Next, place the needle threader, a little hook or wire, near the needle’s eye. Pull the thread through the threader’s loop or turn to make a loop. Gently slide the thread loop through the needle’s eye and pull the yarn end through the loop, leaving a tail for stitching. This approach threads the needle quickly and correctly. Needle threaders differ by sewing machine model, so check your manual for instructions.
FAQ About Sewing Machine Needle Problems
Why is my sewing machine needle skipping stitches?
There are several possible reasons for skipped stitches, including using the wrong needle size or type for the fabric, a bent or dull needle, improper thread tension, or an issue with the machine’s timing. Try troubleshooting these factors to resolve the issue.
What can cause my sewing machine needle to become dull?
Needles can become tedious after prolonged use or if they hit pins, zippers, or other complex objects while sewing. Sewing through thick layers of fabric can also dull the needle. Regularly replacing the needle after every 8-10 hours of sewing or at the start of a new project can prevent dullness.
Why does my sewing machine needle keep breaking?
Several factors can contribute to needle breakages, such as using the wrong needle size or type, improper needle insertion, sewing through thick layers without proper support, using a damaged or worn-out needle, incorrect thread tension, or timing issues with the machine. Addressing these factors can help prevent needle breakage.
Can using the wrong needle size damage my fabric?
Yes, using the wrong needle size can damage your fabric. A too-thick needle can leave noticeable holes or cause fabric puckering. At the same time, a too-thin needle can result in skipped stitches or fabric damage. Always choose the appropriate needle size for your fabric to achieve the best results.
How often should I replace my sewing machine needle?
Replacing your sewing machine needle after every 8-10 hours of sewing or at the start of a new project is recommended. Regularly replacing the needle ensures optimal performance, prevents needle-related issues, and maintains the quality of your stitches.
Can a dull needle affect the quality of my stitches?
Yes, a blunt needle can negatively impact stitch quality. It may cause uneven stitches, fabric puck.
Conclusion
With the information gained from this article, you can successfully troubleshoot and resolve any sewing machine needle problems that may emerge during your sewing endeavors. Suppose you want your sewing projects to turn out well. In that case, taking care of your machine, using the appropriate needle, and developing good habits are essential. Good luck with your needlework!